Lesson Progress
0% Complete
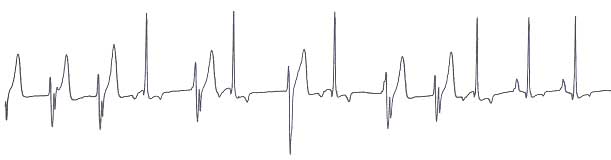
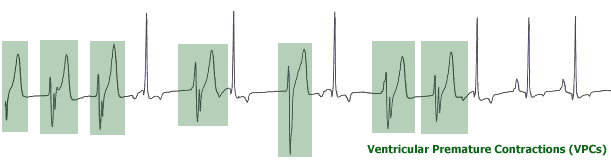
Ventricular premature contractions (VPCs) are depolarizations from an ectopic focus in the ventricular myocardium.
ECG Findings:
- The QRS complexes are usually wide and bizarre.
- If several ectopic foci are present, the morphology of the QRS will vary with each focus (multi-form VPCs).
- Most VPCs are accompanied by a pause or delay after, prior to the onset of the next sinus beat. A time measurement that includes the pause can be used to discriminate between VPCs and SVPCs. For a representation please see diagram under question 33.
- VPCs may occur as fusion and as interpolated beats.
- A fusion beat is a QRS with a morphology that is neither identical to the sinus QRS, nor to a typical VPC. It is also a QRS which occurs on time (i.e. it is not premature). It represents a fortuitous situation wherein part of the ventricular mass was depolarized as a result of the sinus beat and the remainder of the ventricular mass was depolarized as a result of the ectopic ventricular focus.
- An interpolated beat is a special form of VPC wherein the presence of the VPC did not interrupt the underlying sinus rhythm.
Etiology:
- Myocardial disease causing ventricular concentric hypertrophy or eccentric hypertrophy
- Hypoxemic states as anemia, gastric dilation volvulus, heart failure
- Metabolic derangements such as acidosis or hypokalemia
- Trauma (traumatic myocarditis)
- Circulating cytokines in neoplastic and systemic inflammatory disorders
- Drugs such as digoxin, barbiturates, some antiarrhythmic agents
Consequence:
- If enough premature beats are present, cardiac output may fall due to dyssynergy of contraction and high heart rate.
- May predispose to ventricular fibrillation.
Treatment:
- If IV anti-arrhythmic therapy is necessary, choices include lidocaine, procainamide, beta blockers, or in some cases amiodarone, with lidocaine being the first choice.
- Oral anti-arrhythmic choices include mexiletine (lidocaine analog), sotalol, pure beta blockers, or amiodarone
