Bundle branch block is a conduction abnormality whereby an impulse originating from the supraventricular area (sinus node, atria, or AV node) conducts slowly or incompletely (blocks) in one of the two bundle branches (right or left), such that the ventricles are activated non-simultaneously.
The cause may be a structural or functional lesion of one of the bundle branches, or may be physiologic when a premature beat encroaches on the refractory period of the bundle branches.
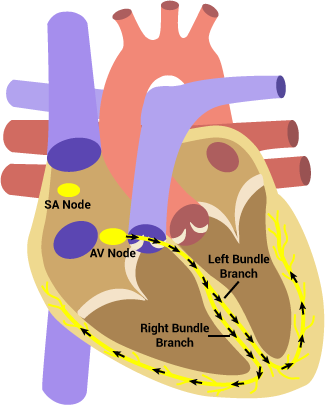
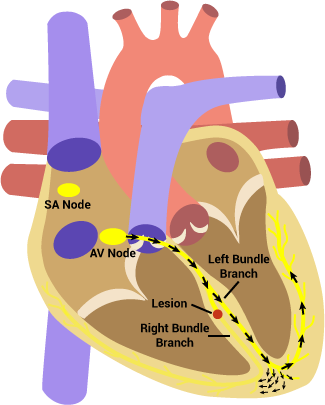
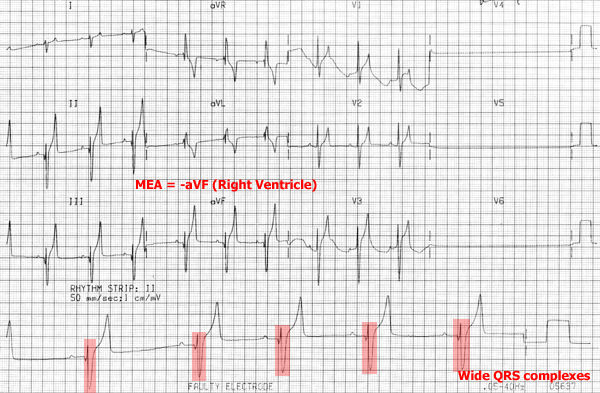
During right bundle branch block there is a lesion along the right bundle branch which prevents normal conduction down to the right ventricle. As a result, the left ventricle depolarizes normally and then its wave of depolarization spreads to the right ventricle from myocyte to myocyte. The depolarization of the ventricles during takes longer to occur, resulting in wider QRS complexes. ECG characteristics:
- Supraventricular origin (associated P waves)
- Wide QRS complexes
- MEA points to RV
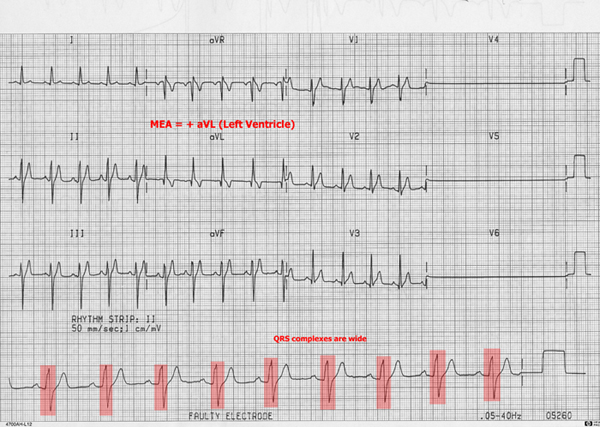
During left bundle branch block there is a lesion along the left bundle branch which prevents normal conduction down to the left ventricle. As a result, the right ventricle depolarizes normally and then its wave of depolarization spreads to the left ventricle from myocyte to myocyte. The depolarization of the ventricles takes longer to occur, resulting in wider QRS complexes. ECG characteristics:
- Supraventricular origin (associated P waves)
- Wide QRS complexes
- MEA points to LV