Back to Course
Cardiovascular Physiology and Pathophysiology
0% Complete
0/0 Steps
-
Physiology
Structure and Function4 Topics -
Lymphatics and Edema Formation
-
The Microcirculation
-
Vascular Control3 Topics
-
The Cardiac Cycle
-
Determinants of Myocardial Performance7 Topics
-
Neuro-Control of Heart and Vasculature4 Topics
-
Electro-Mechanical Association4 Topics
-
Electrical Side of the Heart4 Topics
-
PathophysiologyDefining Heart Failure
-
Causes of Heart Failure
-
MVO2 and Heart Failure
-
Cardiac Output and Heart Failure7 Topics
-
Compensation for Circulatory Failure
-
Vascular Tone in Heart Failure
Lesson 9,
Topic 2
In Progress
Electrical System of the Heart
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
The role of the electrical system of the heart is:
- To maintain an adequate heart rate (proportional to the energy expenditure of the body)
- To coordinate the contraction of the atria and the ventricles in series
- To coordinate the simultaneous contraction of the two atria and subsequently the two ventricles (especially the ventricles)
Components of the electrical system in the heart
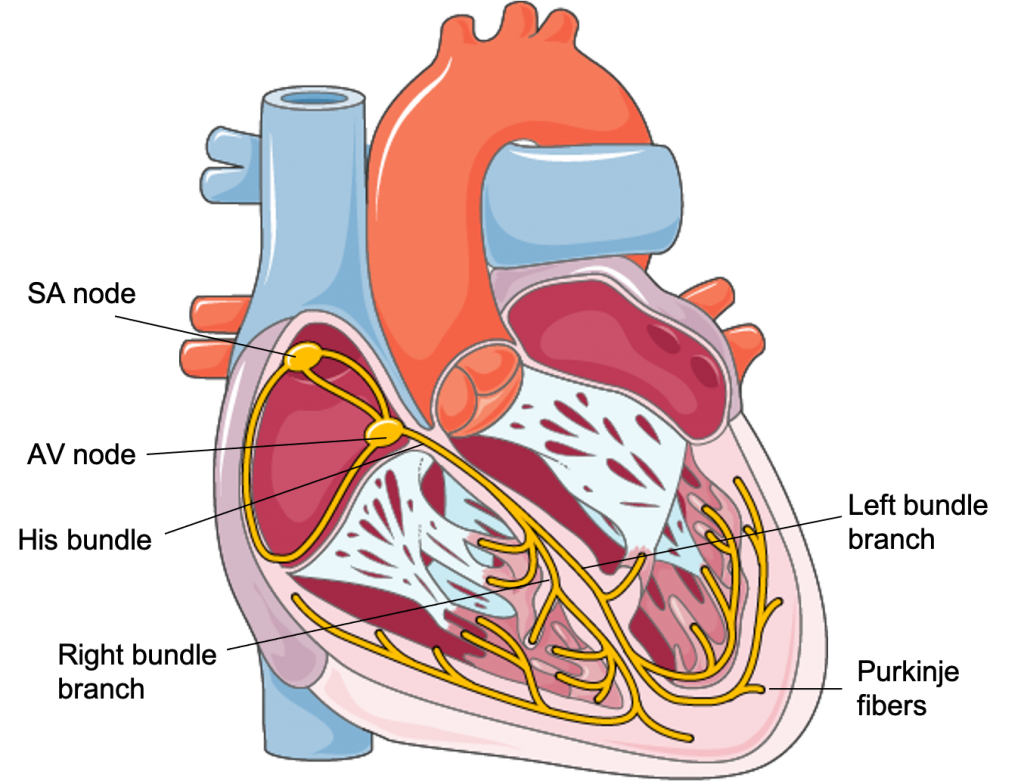
The Sino-Atrial (SA) Node:
- It is the command center for the coordination of all electrical activity
- The cells of the SA node have the property of automaticity (depolarizing spontaneously)
- These cells are under the influence of the autonomic nervous system
- The sympathetic system (beta-adrenergic stimulation) increases the firing rate of the SA node
- The parasympathetic system (acetylcholine stimulation) decreases the firing rate of the SA node
The Atrio-Ventricular (AV) Node:
- It serves as the gateway for electrical transmission between the atria and the ventricles
- It serves to insert an appropriate delay between atrial and ventricular contraction
- It prevents the ventricles from being activated too rapidly in cases of excessively rapid atrial activation
Bundle of His:
- A short segment of “electrical highway” connecting the AV node and the bundle branches
Bundle Branches:
- Left and right bundle branches deliver the electrical current from the bundle of His to the left and right ventricle, respectively
Purkinje Fibers:
- The bundle branches terminate in the myocardial tissue along the endocardium in Purkinje fibers
